
'The idea behind our experiments is simple,' explains Antognini.
ATOMIC RADIUS OF HELIUM FREE
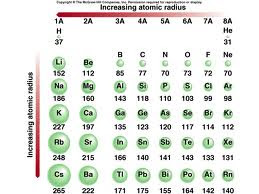
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. According to their findings, the so-called mean charge radius of the helium nucleus is 1.67824 femtometers. From top to bottom in a group, orbitals corresponding to higher. Thus, helium is the smallest element, and francium is the largest. As can be seen in the figures below, the atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group, and decreases from left to right across a period. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. Atomic radii vary in a predictable way across the periodic table. It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The atomic radius of Helium atom is 28pm (covalent radius). Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance. Given the atomic radius of helium, 0.32, and knowing that a sphere has a volume of 4r3/3, calculate the fraction of space that He atoms occupy in a. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. Helium 1's'2 We know that Hydrogen atom has one proton in its nucleus whereas helium atom has two protons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Helium are 3 4. Helium From electron filling of atomic shells we know that the smallest atomic radius will be of the element which has electrons having lowest principal quantum, n1 As such we have only two elements which fill the 1s orbital.
Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.įor stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes.
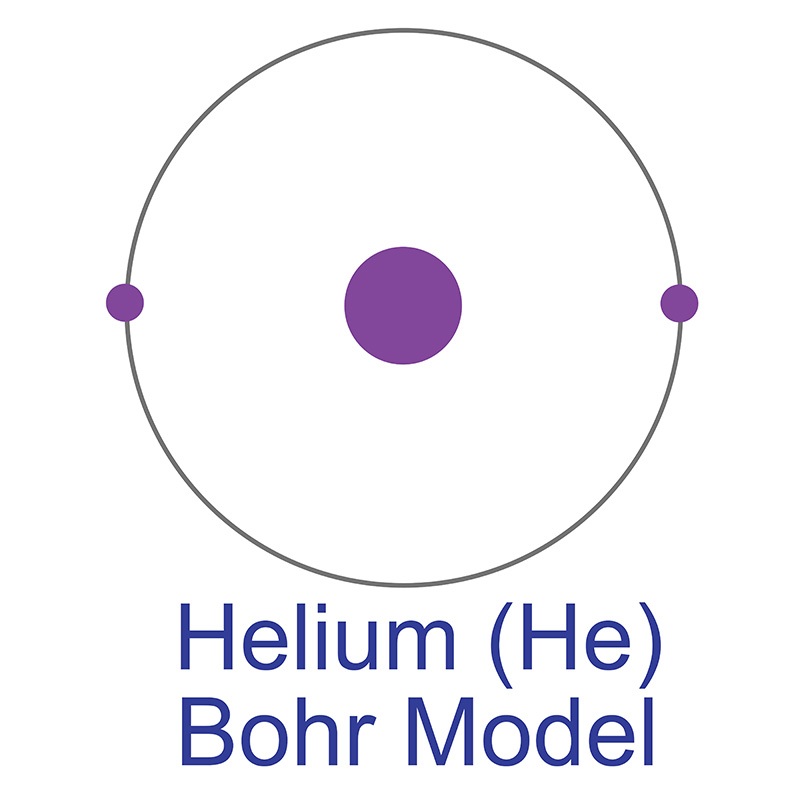
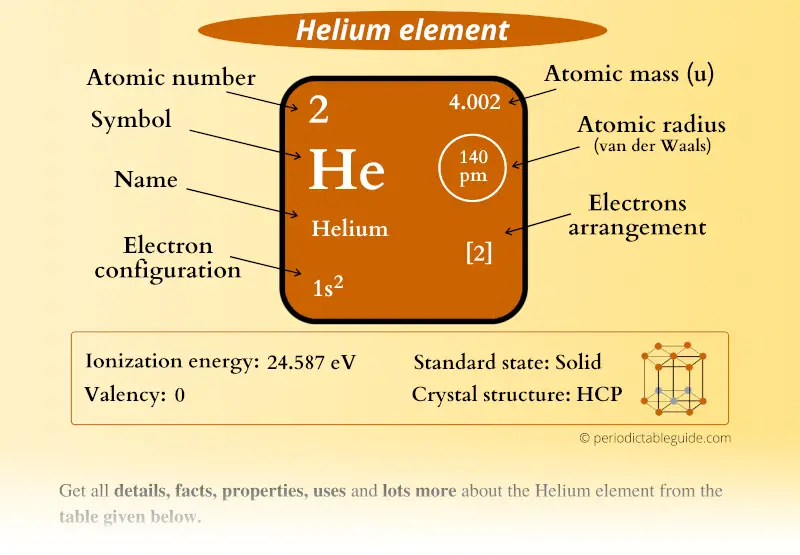
Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons in its nucleus. Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in Helium


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
